Every time you breathe, your body burns the fuel inside your cells and turns it into energy.
This energy runs your cells to create millions of chemical reactions required to be alive. This mixing of oxygen and fuel to create energy is known as “Oxidation”.
This process of oxidation creates dangerous byproducts known as free radicals. Free radicals are extremely dangerous because they’re like bullies that beat up on other cells and steal their vital electrons. They do this because they are missing an electron as a result of oxidative damage.
Electrons come in pairs, so free radicals try to stabilize themselves by stealing an electron from another oxygen molecule.
Free radicals can cause extensive damage to the body because once they steal another molecule´s electron, it becomes unstable. This one as well becomes a free radical and attacks nearby cells to steal electrons.
The process continues in a chain reaction and can bring extensive chaos through-out the body.
In a healthy person who has a healthy diet, free radicals remain relatively controlled thanks to a constant supply of antioxidants. These antioxidants travel throughout the body, donating electrons where needed. This effort stabilizes free radicals and prevents free radical attacks to cells.
In addition, antioxidants provide nutrients to help damaged cells repair themselves.
When the cells are too damaged to repair, the nutrients trigger a cellular suicide, a natural process known as apoptosis. This keeps the body free of mutated cells that may cause further harm and even lead to sickness.
So when does oxidative stress become a problem?
Much like inflammation, health issues develop when the body becomes overrun by free radicals and can’t keep up with the damage they‘re inflicting. At this point, the damage is known as oxidative stress.
Your body has more oxidative damage than you may think.
Simply living a modern lifestyle creates more free radicals than the body can control.
They come from:
Food chemicals
preservatives, artificial colorings and flavorings, processed foods, refined sugar, etc.
Environmental pollutants
including pesticides, petrochemicals, asbestos, industrial plant emissions, etc.
Air pollution
from car exhausts, smog and other toxic fumes.
Smoking
or inhaling second-hand smoke.
Radiation
from the sun, tanning lamps, medical x-rays, high-definition electronics, computer screens, etc.
Household chemicals
found in cleaners, pesticides, formaldehyde, personal care products, room deodorizers, etc.
Alcohol
any amount of alcoholic beverage creates free radicals.
Cured meats
nitrates and nitrites used to preserve packaged or cured meats.
Medications
pharmaceutical drugs, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, x-rays.
Stress
both emotional (worry and stress) and physical (over-exercising or injury).
Inflammation
causes oxidized cells to rupture and spread more damage throughout the body.
Your health starts decaying when your body becomes overrun by free
radicals and can’t keep up with the destruction they’re causing.
Unfortunately, even healthy people should be aware of the dangers of oxidative stress.
It‘s estimated that free radicals attack your cells every 10 seconds.
When you multiply that to the over 37 trillion cells in the
human body, that’s…
600 quadrillion attacks (600,000,000,000,000,000)
a day terrorizing your body and brain!
And as if all those attacks aren’t enough, we also produce more free radicals as we age. Eating more fruits and vegetables is no longer good enough.
At risk is also the brain, an organ that utilizes large amounts of oxygen.
To see how oxidative stress breaks down our bodies, cut an apple in half. Within minutes, you’ll see oxidation begin to turn the apple brown in some spots. The same thing occurs in the cells of the body when oxidative stress is not controlled.
That’s Oxidation.
And this explains how we age!
How to reduce Oxidative stress?
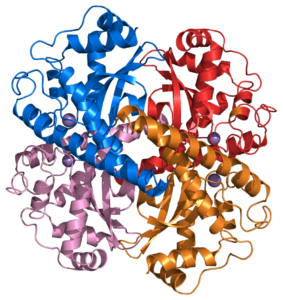
The first shield against oxidative stress is the superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzyme. It protects all forms of life exposed to oxygen from oxidation for over 2 billion years.
SOD plays a critical role in preventing Oxidative stress:
It is the only antioxidant agent able to control the production of ROS and prevent cell oxidation! The Key Factor in maintaining Youthfulness and Good Health!